Here is the rewritten article in HTML format:
Introduction
The increasing trend of robots being integrated into human-centered environments has brought about a new challenge: the need for mobile manipulation and compliant control. In unstructured, dynamic environments where humans and robots coexist, compliance is crucial for ensuring robust performance and safety.
The Rise of Compliance
Compliance refers to a robot’s ability to interact with its environment in a flexible and adaptable manner. This can be achieved through indirect force control methods such as admittance and impedance control. Admittance control enables the robot to adapt its behavior based on sensed forces, allowing it to yield or move in response to external forces. Impedance control regulates the robot’s interaction with its environment by managing the relationship between applied forces and resulting movements, effectively acting as a “stiffness” to external forces.
A Cost-Effective Approach
The Autonomous Multi-Robots Lab at the Delft University of Technology has been working on a cost-effective approach to address compliance for mobile manipulators and velocity-controlled mobile bases without adding force/torque sensors.
Dingo-O: The Ideal Platform for Human-Centered Environments
The team used Dingo-O for their base as part of the mobile manipulator. Dingo-O is a sleek, lightweight, omni-directional indoor platform ideal for human-centered environments.
Impedance Control without Force/Torque Sensors
Using the mobile manipulator, the team developed a calibration method that would enable the application of impedance control on current-controlled manipulators without force/torque sensors. This method estimates the direct correlation between the actuator current and the resulting joint torque, as well as the friction encountered by the arm as it moves its joints. It utilizes the robot’s model and earth’s gravity to estimate the ratio between the actuator current and the resulting torque. Furthermore, the calibration method also incorporates techniques to adjust for Center of Mass (COM) displacements, ensuring that the robot’s behavior is accurately modeled and controlled.
Two Operational Modes
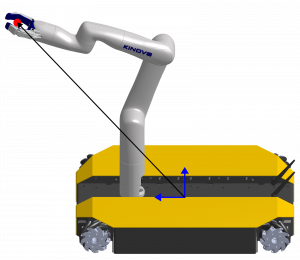
Figure 1: Guidance Mode
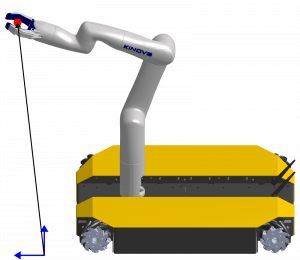
Figure 2: Tracking Mode
A Triumph In Compliance-Drive Mobile Manipulation
The team was able to develop a holistic, cost-effective approach to addressing compliance for mobile manipulators using off-the-shelf parts. They were able to introduce a calibration method that enables the application of impedance control on current-controlled manipulators, and therefore no force/torque sensors are required.
Demonstrating the reliability of their method, the team was able to present two operational modes for interacting with the mobile manipulator. This allowed a human to guide the robot through interaction with the manipulator and expand the manipulator’s operational range. The compliance of the impedance controller was validated, showcasing its ability to track a target with precision, achieving accuracy within a 5 mm range when uninterrupted by external forces.
Their work not only promotes cost-effectiveness, accessibility, and adaptability using off-the-shelf parts but also significantly enhances the usability and efficacy of mobile manipulation in real-world scenarios such as collaborative robotics and assistive applications.
Conclusion
The Autonomous Multi-Robots Lab at the Delft University of Technology has successfully demonstrated a cost-effective approach to addressing compliance for mobile manipulators using off-the-shelf parts. Their work has the potential to significantly enhance the usability and efficacy of mobile manipulation in real-world scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is impedance control?
Impedance control is a type of control method that regulates the interaction between a robot and its environment by managing the relationship between applied forces and resulting movements, effectively acting as a “stiffness” to external forces.
How does impedance control improve compliance?
Impedance control improves compliance by enabling a robot to interact with its environment in a flexible and adaptable manner. This allows the robot to adapt to external forces and move in response, effectively improving its ability to interact with humans and objects in a real-world environment.
What is a calibration method?
A calibration method is a technique used to estimate the direct correlation between the actuator current and the resulting joint torque, as well as the friction encountered by the arm as it moves its joints. This information is then used to accurately model and control the robot’s behavior.
What is the significance of using off-the-shelf parts?
Using off-the-shelf parts can significantly reduce the cost and increase the accessibility of a robot, making it more viable for real-world applications such as collaborative robotics and assistive technologies.
What is the potential of mobile manipulation?
The potential of mobile manipulation is significant, with the ability to expand the operational range of a robot and enable it to interact with humans and objects in a real-world environment. This technology has the potential to significantly enhance the usability and efficacy of robots in various applications, including healthcare, manufacturing, and education.
Who were the team members involved in this research project?
The team members involved in this research project include Jelmer de Wolde (Master student, graduated), Luzia Knoedler (PhD student), Saray Bakker (PhD student), Andreu Matoses Gimenez (PhD student), and Javier Alonso-Mora (associate professor).





